|
Examples of Our Work Interactive visual information processing, interactive
image retrieval, segmentation .... (link ...) Example-based
Image Processing ... Unifying histogram-based image content descriptor for
content-based image retrieval - the CPAM and AI framework
... (link ...) Integrated framework for image coding, indexing, and
content-based image retrieval ... (link ...) Visual guided browsing and navigation for fast image
retrieval ... (link ...) Fast comprehensive tone mapping for high dynamic range
image visualization ... (link ...) Colorizing black and white photos ... (link ....) Making beautiful pictures, computational
photography ... (link ....) Machine learning, pattern recognition ... (link ...) Image data mining, image and feature co-clustering .... (link ...) |
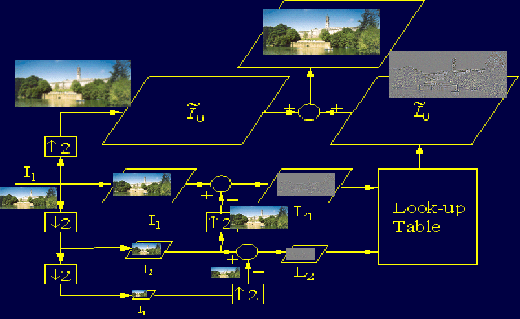 Schematics of our example-based image super-resolution system |
|
Example-based
Image Processing We are one of the first groups to propose example-based
or learning based image processing technologies. We have developed
several lines of application in this area from image
super-resolution and coding artifact
filtering/removal to the display of high dynamic
range image.
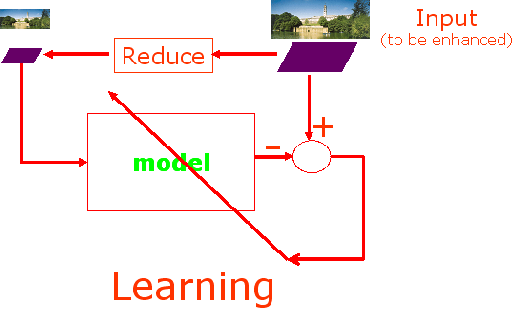 Our technique first learns a model that takes a lower resolution version of an image as input and predict a higher resolution version of the same image as output. 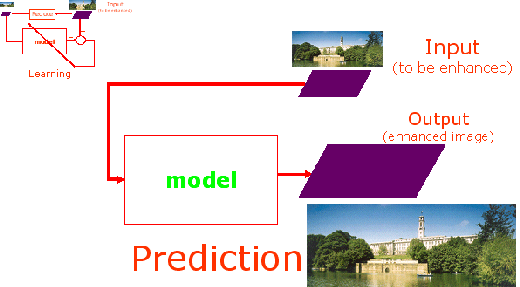 Once the model is learned, it is used to predict a higher resolution output from a lower resolution input.  In order to reduce the burden on the learner, we use a smooth prior, i.e., we learn the Laplacian image and add it back to the Gaussian image. For more detail, please refer to the publications listed above. Work by others that learns to enhance image resolution include the following: References
Learning-based Approach to Image Coding Artifact Removal 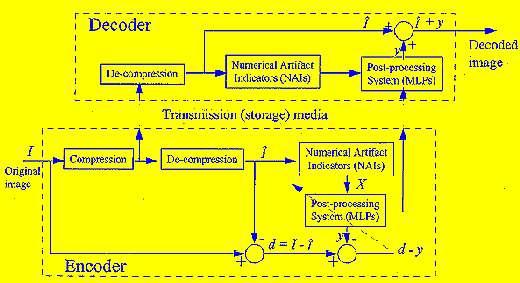 G. Qiu, "MLP for adaptive postprocessing block coded images", IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 10, pp. 1450 - 1454, Decemner, 2000 (PDF) We have developed a
method based on the concept of learning-by-examples for
blocking-artifact removal in block-coded images. In the developed
scheme, inter-block slopes of the compressed image are used as input,
the difference between the original uncompressed and the compressed
image is used as desired output for training neural networks.
Blocking-artifact removal is realized by adding the neural network’s
outputs to the compressed image. The new technique has been applied to
process JPEG compressed images. Experimental results show significant
improvements in both visual quality and peak signal-to-noise ratio. It
is also shown the present method is comparable to other state of the
art techniques for quality enhancement in block-coded images.
Learning to display high dynamic range images  J. Duan, G. Qiu and G. D. Finlayson,"Learning to display high dynamic range images", CGIV'2004, IS&T's Second European Conference on Color in Graphics, Imaging and Vision, Aachen, Germany, April 5-8, 2004 (PDF) We have developed a learning based method to map high dynamic range scenes to low dynamic range images for visualization. We formulate the problem as a quantization process and employ an adaptive learning strategy to ensure that the low dynamic range displays not only faithfully reproduce the original scenes but also are visually pleasing. This is achieved by the use of a competitive learning neural network that employs a frequency sensitive competitive learning mechanism. |