The HyFlex Framework
- General Description
- Problem Domain Modules
- HyFlex Software Documentation (API Document)
General Description
HyFlex (Hyper-heuristics
Flexible
framework) is a Java object oriented framework for the
implementation
and
comparison of different iterative general-purpose heuristic
search
algorithms (also called hyper-heuristics). The framework
appeals to
modularity and the idea of decomposing a heuristic search
algorithm
into two main parts (Figure 1):
- A general-purpose part: the competing algorithms or hyper-heuristics
- The problem-specific parts: provided by the HyFlex framework
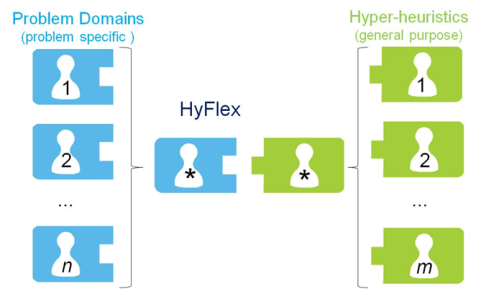
Figure 1: Modularity
of heuristic search
algorithms. Separation between the
problem-specific and the general-purpose parts, both of
which are
reusable and interchangeable through the HyFlex interface.
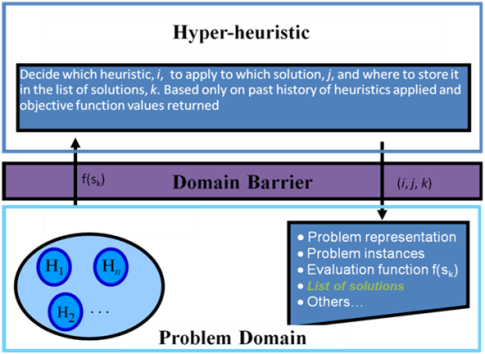
Figure 2: The
hyper-heuristic framework featuring the domain barrier,
the
hyper-heuristic layer and the problem domain layer.
[Top]
Problem Domain Modules
Each HyFlex problem domain module consists of:- A routine to randomly initialise solutions.
- A set of low level heuristics to modify solutions, each classified into one of four groups:
- Mutational or perturbation heuristics: perform a small change on the solution, by swapping, changing, removing, adding or deleting solution components.
- Ruin-recreate (destruction-construction) heuristics: partly destroy the solution and rebuild or recreate it afterwards. These heuristics can be considered as large neighbourhood structures. They are, however, different from the mutational heuristics in that they can incorporate problem specific construction heuristics to rebuild the solutions
- Hill-climbing or local search heuristics: iteratively make small changes (mutations or perturbations) to the solution, accepting improving or non-deteriorating solutions, until a local optimum is found or a stopping condition is met. These heuristics differ from mutational heuristics in that they incorporate an iterative improvement process; therefore they guarantee that a non-deteriorating solution will be produced.
- Crossover heuristics: take two solutions, combine them, and return a new solution.
- A varied set of instances that can be easily loaded using the method loadInstance(a), where a is the index of the instance to be loaded.
- A user-configurable memory (a population) of solutions, which can be managed by the hyper-heuristic
- Two parameters: α and β, (0 ≤ [α, β] ≤ 1), which are the "intensity" of mutation and "depth of search", respectively, that control the behaviour of some low level heuristics.
Test Problem Domains Provided
Currently, the HyFlex framework provides the following four test domains (follow the links for more details on each of them):- Boolean Satisfiability (MAX-SAT)
- One Dimensional Bin Packing
- Permutation Flow Shop
- Personnel Scheduling (see also the Staff Rostering Benchmark Data Sets)
[Top]
Last Updated: 25 May 2011, by Gabriela Ochoa.
